Can You Update Jslint In Webstorm
WebStorm integrates with ESLint which brings a wide range of linting rules that tin also be extended with plugins. WebStorm shows warnings and errors reported by ESLint right in the editor, as you type. With ESLint, y'all tin also use JavaScript Standard Style as well as lint your TypeScript code.
Besides JavaScript and TypeScript, ESLint tin exist applied to files of other types in the unabridged project or in its specific parts, run across Configure linting scope.
Earlier yous start
-
Brand sure yous have Node.js on your computer.
-
Make sure a local Node.js interpreter is configured in your project: open the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) and go to . The Node Interpreter field shows the default project Node.js interpreter.
Learn more from Configuring a local Node.js interpreter.
Install ESLint
-
In the embedded Last (Alt+F12) , type one of the following commands:
-
npm install --g eslintfor global installation. -
npm install --save-dev eslintto install ESLint equally a development dependency.
-
-
Optionally, install additional plugins, for example, eslint-plugin-react to lint React applications.
Activate and configure ESLint in WebStorm
By default, ESLint is disabled. You can choose to configure information technology automatically or specify all the configuration settings manually.
Configure ESLint automatically
With automatic configuration, WebStorm uses the ESLint parcel from the projection node_modules folder and the .eslintrc.* configuration file from the binder where the current file is stored. If no .eslintrc.* is found in the current file folder, WebStorm volition look for i in its parent folders up to the project root.
If yous have several package.json files with ESLint listed every bit a dependency, WebStorm starts a separate process for each package.json and processes everything below information technology. This lets y'all apply a specific ESLint version or a specific gear up of plugins to each path in a monorepo or a project with multiple ESLint configurations.
-
To configure ESLint automatically in the electric current project, open up the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+South), go to , and select the Automatic ESLint configuration option.
-
To configure ESLint automatically in all new projects, open up the Settings for New Projects dialog () , go to , and select the Automatic ESLint configuration option.
Configure ESLint manually
With transmission configuration, you can use a custom ESLint package, configuration file, and working directories, as well every bit apply various additional rules and options.
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+South), get to , and select Manual ESLint configuration.
-
In the ESLint bundle field, specify the location of the eslint or standard package.
-
In the Working directories field, specify the working directories for the ESLint process.
By default the field is empty and WebStorm detects the working directory automatically. Kickoff it looks for a directory closest to the linted file which contains a .eslintignore or .eslintrc.* file, or a package.json file with either a
eslintIgnoreor aeslintConfigproperty.If the auto-detected working directory doesn't match your project configuration, you demand to specify the working directory (directories) manually. Use semicolons equally separators. The acceptable values are:
-
Absolute paths.
-
Paths relative to the project base directory (the parent folder of the .idea folder where WebStorm-specific project metadata is stored). For instance:
-
./- use project base directory equally ESLint process working directory. -
customer;server- use the <project_base_dir>/client and <project_base_dir>/server as working directories. For files that are neither under the client non under the server binder, the working directory will exist motorcar-detected as described above. -
packages/*- each subfolder of the <project_base_dir>/packages binder will exist used equally the working directory for the respective linted files.
-
-
Paths relative to the content roots tin exist used if some linted files are non nether project base directory in the folder hierarchy.
-
Glob patterns that define relative paths to the working directories. For example, with
**/foo -*each folder with the proper name starting withfoo-volition exist used as the working directory for the corresponding linted files.
-
-
Choose the configuration to utilize.
-
Automatic search - select this pick if ESLint rules are configured in a package.json or in a .eslintrc.* file. This can be a .eslintrc, .eslintrc.json, or .eslintrc.yaml file, or a file in another supported format, encounter the ESLint official website for details.
WebStorm looks for a .eslintrc.* file or for a
eslintConfigproperty in a bundle.json. WebStorm starts the search from the folder where the file to be checked is stored, and so searches in its parent folder, and so on until the projection root is reached. -
Configuration File - select this option to apply a custom file and specify the file location in the Path field.
Learn more about configuring ESLint from the ESLint official website.
-
-
Optionally:
-
In the Extra eslint options field, specify additional command-line options to run ESLint with, use spaces as separators.
Larn more about ESLint CLI options from the ESLint official website.
-
In the Additional rules directory field, specify the location of the files with additional lawmaking verification rules. These rules will be applied after the rules from parcel.json, .eslintrc.*, or a custom configuration file and accordingly will override them.
See the ESLint official website for more information about ESLint configuration files and calculation rules.
-
Configure linting telescopic
-
Open up the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+Southward), get to , and select Automated ESLint configuration or Manual ESLint configuration.
-
In the Run for files field, specify the pattern that defines the prepare of files to be linted. You tin can accept the default pattern or type a custom one.
With the default blueprint,
{**/*,*}.{js,ts,jsx,tsx,html,vue}, ESLint volition wake up and process any updated JavaScript, TypeScript, JSX, TSX, HTML, or Vue file. To lint files of other types or files stored in specific folders, use glob patterns to update the default pattern.-
For example, to automatically reformat CoffeeScript files besides, add together
coffeeto the default blueprint equally follows:{**/*,*}.{js,ts,jsx,tsx,html,vue,coffee}
-
To lint files from a specific folder, supplant
{**/*,*}with<path to the binder>*.Suppose, you have a project with the following structure:
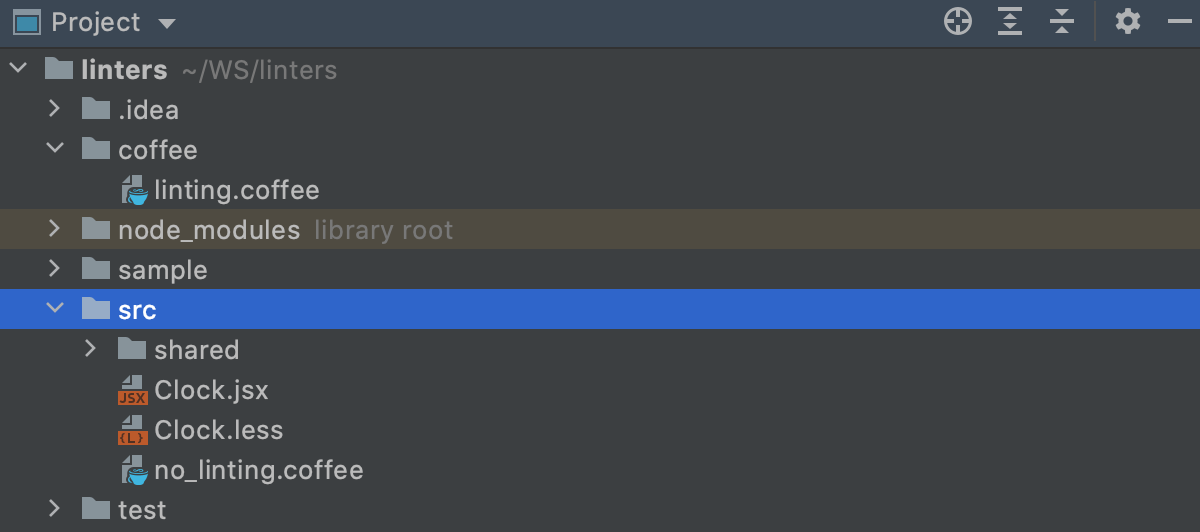
To lint only the files in the coffee binder, update the pattern as follows:
coffee/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx,html,vue,java}
Every bit a result, the file linting.coffee volition be linted while no_linting.coffee will non.
-
Fix problems automatically on save
ESLint can fix the detected problems every time your changes are saved either manually, with Ctrl+Due south, or automatically, when y'all launch a run/debug configuration, or close WebStorm, or perform version control deportment, see Autosave for details.
-
Open the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), become to , and select the Run eslint --prepare on save checkbox.
Lint your lawmaking
When installed and enabled, ESLint activates automatically every fourth dimension you open up a JavaScript file.
By default, WebStorm marks detected problems based on the severity levels from the ESLint configuration. See Configuring ESLint highlighting to learn how to override these settings.
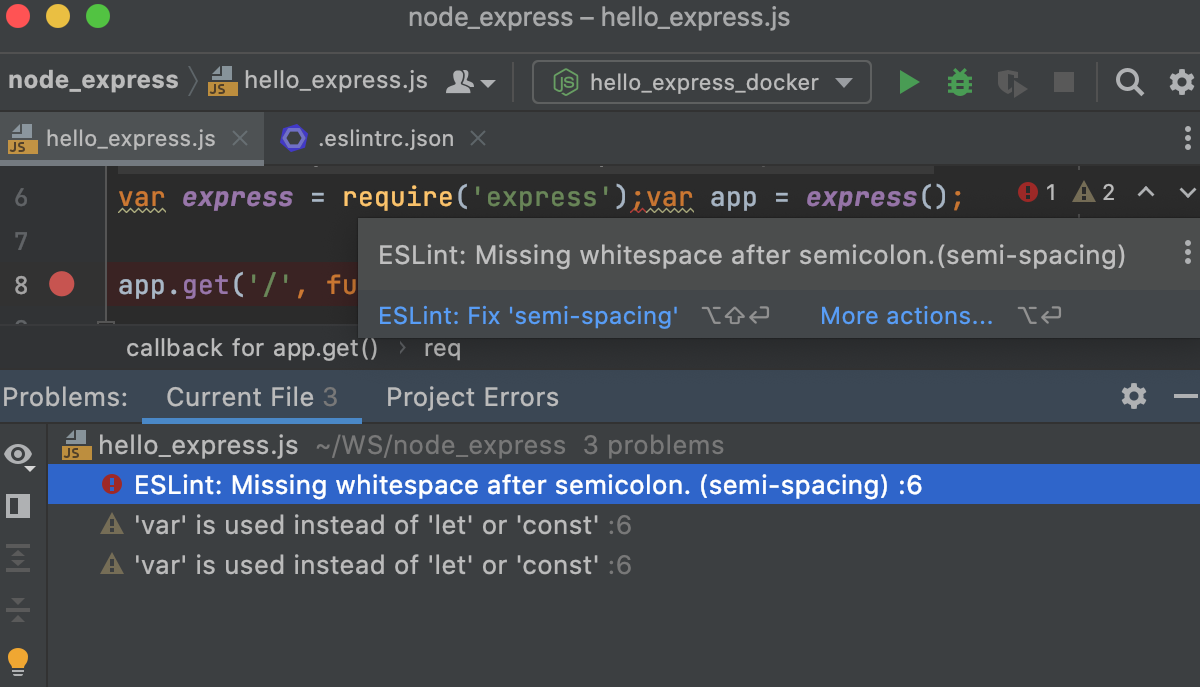
Descriptions of the errors detected in the electric current file and quick-fixes for them are bachelor from the editor and from the Electric current File tab of the Problems tool window.
Errors in all previously opened files and quick-fixes for them are shown in the Project Errors tab of the Bug tool window. To open the tool window, click the Inspection widget in the upper-right corner of the editor:
![]()
Run into View issues and apply quick-fixes in the editor and Bug tool window for details.
View problems and utilize quick-fixes in the editor
-
To view the description of a trouble, hover over the highlighted code.
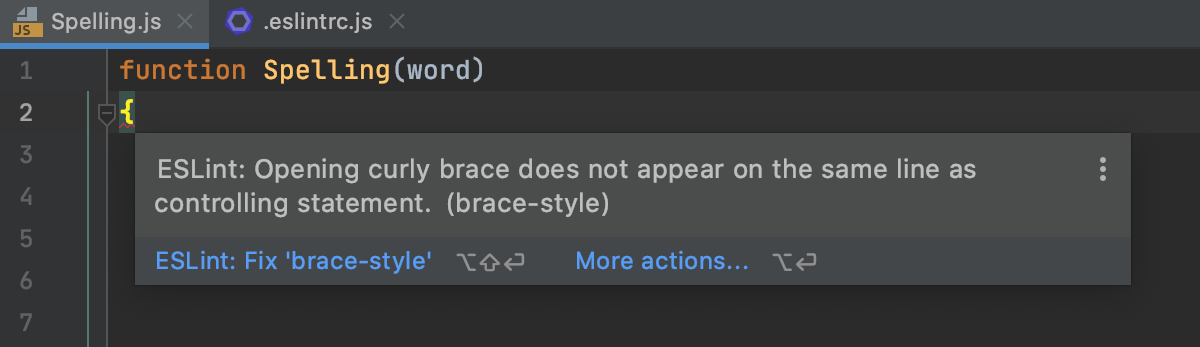
To resolve the detected problem, click ESLint: Set up '<rule name>' or press Alt+Shift+Enter.
To resolve all the detected issues in the current file, click More actions (Alt+Enter) and select from the list.
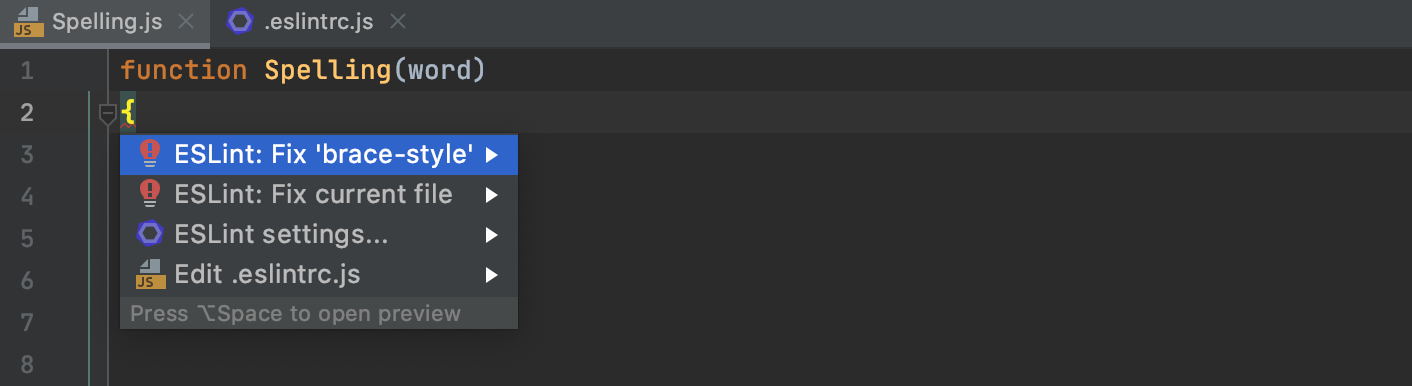
See View problems and apply quick-fixes in the editor for details.
-
Alternatively open the Current File tab of the Problems tool window Alt+6, where yous can view problem descriptions, apply quick-fixes, navigate to the fragments in the source lawmaking where errors occurred, as well every bit fix them in the Editor Preview pane without leaving the tool window. Learn more from Issues tool window.
-
You tin can also configure ESLint to fix all the problems in a file when this file is saved. To configure such behavior, select the Run eslint --set up on save checkbox on the ESLint folio of the Settings dialog every bit described in Activating and configuring ESLint in WebStorm.
Lint your code in the Problems tool window
To open the Problems tool window, click the Inspections widget in the upper-right corner of the editor.
![]()
Alternatively select from the main card or press Alt+half dozen.
The Projection Errors tab shows the errors in all files that were opened during the current session, with error letters grouped by files in which they were detected.
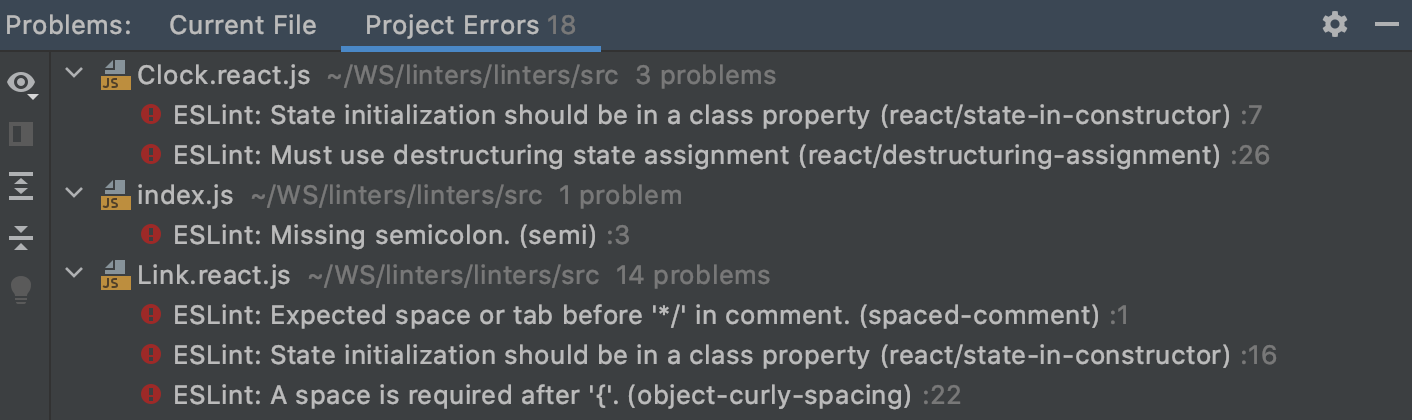
Here you lot can view problem descriptions, apply quick-fixes, navigate to the fragments in the source code where errors occurred, equally well as set them in the Editor Preview pane without leaving the tool window. Larn more than from Problems tool window.
Configure highlighting for ESLint
By default, WebStorm marks the detected errors and warnings based on the severity levels from the ESLint configuration. For instance, errors are highlighted with a reddish squiggly line, while warnings are marked with a yellowish groundwork. See Lawmaking inspections and Change inspection severity for details.
Change the severity level of a dominion in the ESLint configuration
-
In .eslintrc or under
eslintConfigin bundle.json, locate the rule you want to edit and set its ID to1warnor to2error.Acquire more from the ESLint official website.
Y'all tin override the severities from the ESLint configuration so that WebStorm ignores them and shows everything reported by the linter equally errors, warnings, or in a custom color.
Ignore the severity levels from the configuration
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), select . The Inspections page opens.
-
In the cardinal pane, get to JavaScript | Code quality tools | ESLint.
-
In the right-manus pane, clear the Use rule severity from the configuration file checkbox and select the severity level to use instead of the default one.
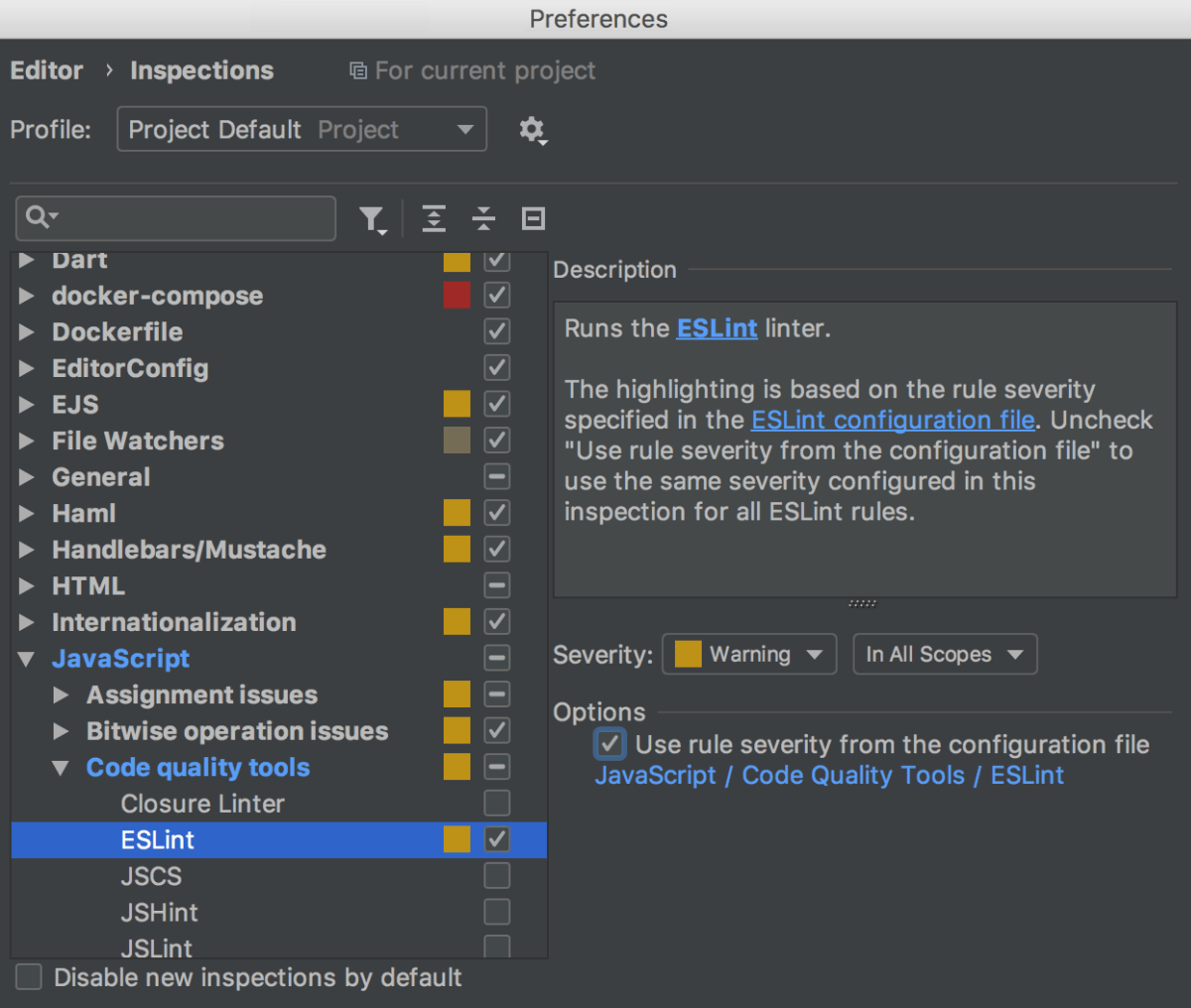
Import code style from ESLint
Y'all tin can import some of the ESLint code style rules to the WebStorm JavaScript lawmaking mode settings. That enables WebStorm to use more than accurate lawmaking style options for your project when car-completing, generating, or refactoring the code or adding import statements. When you use the Reformat activeness, WebStorm will so no longer interruption properly formatted lawmaking from the ESLint perspective.
WebStorm understands ESLint configurations in all official formats: .eslintrc JSON files, package.json files with the eslintConfig field, too every bit JavaScript and YAML configuration files.
-
When you open up your projection for the kickoff time, WebStorm imports the lawmaking way from the project ESLint configuration automatically.
-
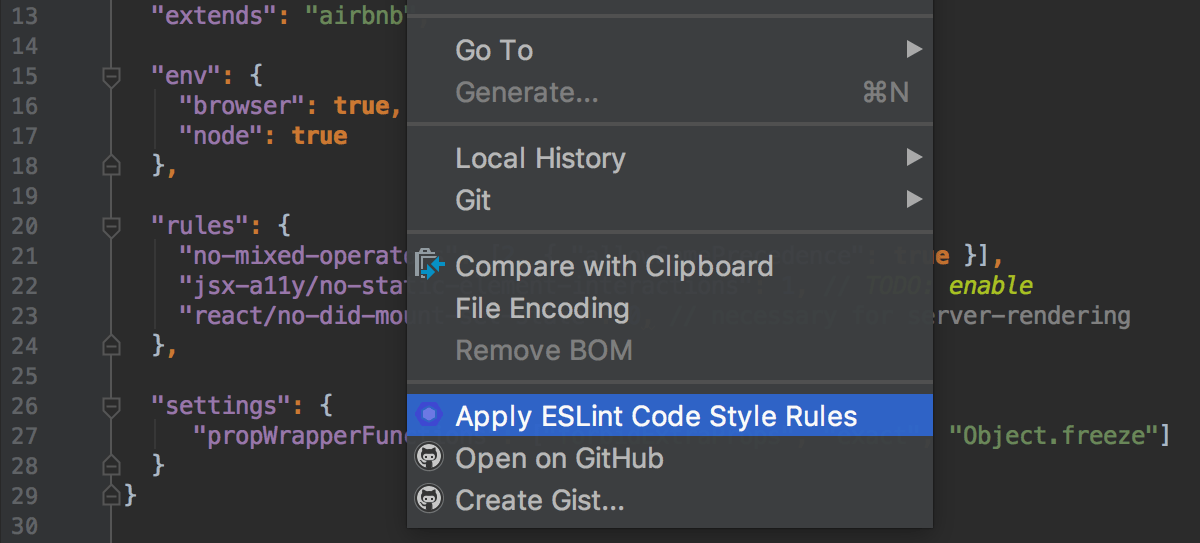
If your ESLint configuration is updated (manually or from your version command), open up it in the editor and cull Utilize ESLint Lawmaking Manner Rules from the context carte du jour.
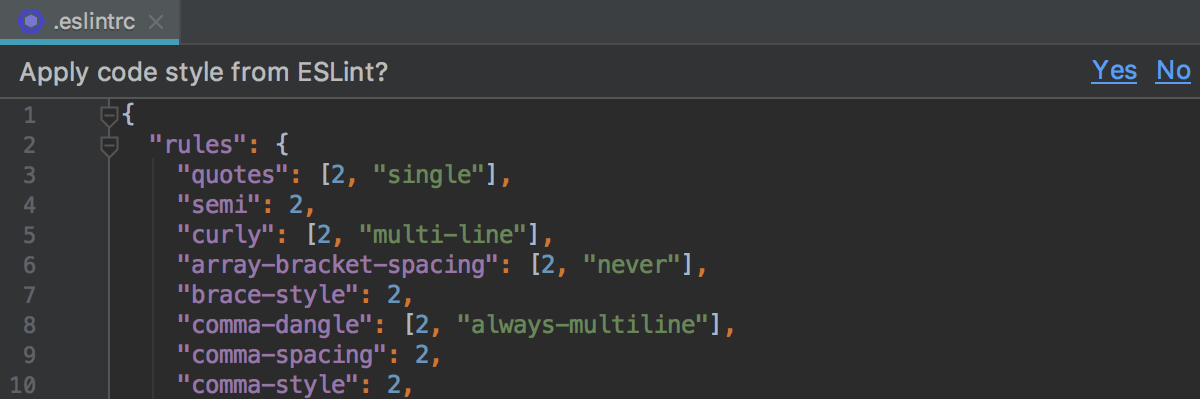
Alternatively, just reply Yep to the "Apply code fashion from ESLint?" question on top of the file.
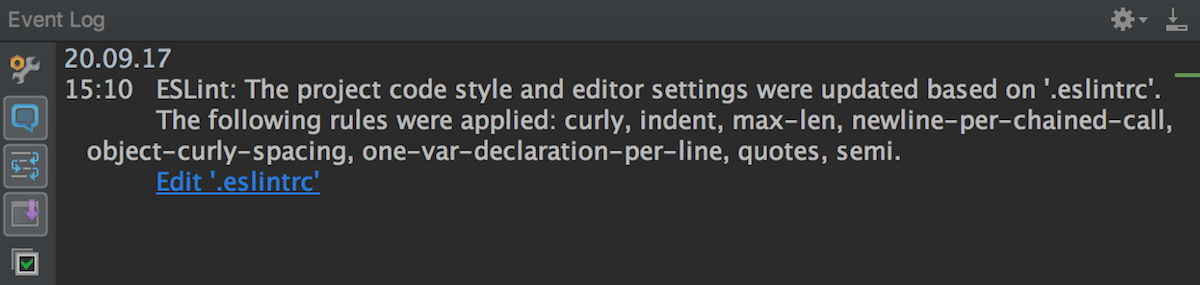
The listing of applied rules is shown in the Consequence log tool window:
Utilise JavaScript Standard Style
You tin can set up JavaScript Standard Style every bit default JavaScript code style for your application so its master rules are practical when you lot blazon the code or reformat it. Since Standard is based on ESLint, y'all can likewise utilise Standard via the WebStorm ESLint integration.
Install JavaScript Standard
-
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install standard --save-devAcquire more than from the JavaScript Standard Style official website.
Enable linting with Standard via ESLint
If y'all open a project where standard is listed in the project'due south package.json file, WebStorm enables linting with Standard automatically.
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+South), become to .
-
On the ESLint page that opens, select Manual ESLint configuration and specify the location of the
standardpackage in the ESLint Package field.
Set the JavaScript Standard Style equally default
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+Southward), go to .
-
On the Code Style. JavaScript page that opens, click Set from, and then select JavaScript Standard Style. The style will replace your current scheme.
ESLint with Docker
With WebStorm, y'all can run ESLint against your code inside a Docker container but in the aforementioned way as you do it locally.
Learn more from Node.js with Docker.
-
Make sure the Node.js, Node.js Remote Interpreter, and Docker required plugins are enabled on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page, tab Installed, see Managing plugins for details.
-
Download, install, and configure Docker equally described in Docker
-
Configure a Node.js remote interpreter in Docker and prepare it is equally default in your project. Also make certain the parcel manager associated with this remote interpreter is set as projection default.
-
Open up your package.json and make sure ESLint is listed in the
devDependenciesdepartment:{ "name": "node-express", "version": "0.0.0", "private": truthful, "dependencies": { "cookie-parser": "~1.4.4", "debug": "~2.6.9", "express": "~4.xvi.1", "http-errors": "~ane.6.3", "morgan": "~1.9.1", "pug": "^3.0.two" }, "devDependencies": { "eslint": "^viii.1.0" } }
-
Right-click anywhere in the editor and select Run '<packet manager> install' from the context bill of fare.
-
After that, ESLint works in the same fashion every bit when you piece of work with your code locally. View descriptions of detected discrepancies right in the editor or in the Problems tool window and apply suggested quick-fixes.
Concluding modified: ten Dec 2021
Source: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/webstorm/eslint.html
Posted by: gilhiseently86.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can You Update Jslint In Webstorm"
Post a Comment